Manufacturer of pipe technology solutions
- Any Questions?[email protected]
- Get in Tough+86-13601562675
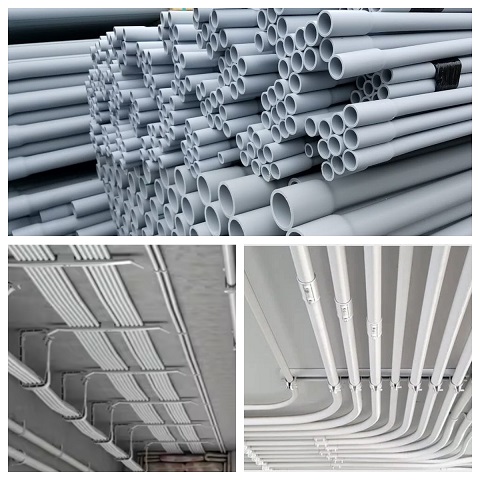
1. Characteristics of PVC Conduit
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) conduit is widely used for electrical wiring protection due to its exceptional properties:
Electrical Insulation & Flame Retardancy: Provides reliable protection for wires and cables with high dielectric strength and self-extinguishing characteristics, ensuring safety in electrical systems
Chemical Resistance & Durability: Resists corrosion from acids, alkalis, and moisture, with a service life exceeding 50 years under normal conditions
Lightweight & Easy Installation: Weighs significantly less than metal conduits, simplifying transportation and on-site handling. Its thin wall design (under equal pressure) further reduces weight
Mechanical Strength: Withstands external pressure and low-temperature bending without cracking, suitable for both exposed and embedded installations (e.g., in concrete)

2. Production Process Flow
Raw Material Preparation: PVC resin, stabilizers, plasticizers, and flame retardants are precisely mixed
Conveying & Feeding: The mixture is transported to a forced feeder for consistent material supply
Extrusion: A conical twin-screw extruder melts and homogenizes the material, then pushes it through a die to form the conduit shape
Sizing & Cooling: Calibration Sleeve: Sets the outer diameter of the conduit.
Vacuum Sizing Tank: Uses vacuum and water spray to stabilize the shape
Printing & Traction: An ink printer laser printer marks specifications (e.g., diameter, standard compliance), followed by a track tractor pulling the conduit at a steady speed
Cutting & Stacking: A cutter trims the conduit to fixed lengths, which are then stacked on a rack for quality inspection and packaging
Pipe Socket Forming:It is designed for forming U-type straight sockets at the end of extruded
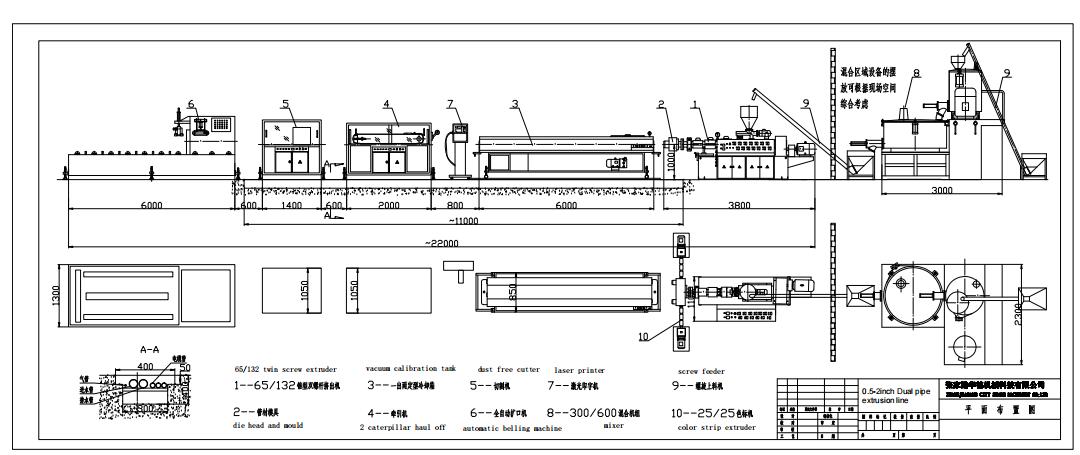
3. Equipment Composition
A typical PVC 4 Strand conduit production line includes the following key components:
Component | Function |
Conical Twin-Screw Extruder
| Melts and extrudes raw materials; models like SJSZ65/132 are common for 16–50mm conduits |
Extrusion Die
| Shapes the molten PVC into the desired conduit profile. |
Calibration & Cooling System
| Includes calibration sleeve, vacuum sizing tank, and cooling to ensure dimensional accuracy |
Belt Haul-off Unit
| Track-type tractor with (inverter speed control) for stable pulling |
Cutting Device | Dust free cutter or guillotine cutter for precise length control |
Socket Forming
| Shaping the conduit end into a precise straight socket (U-type) with uniform wall thickness, ensuring tight sealing and mechanical strength during installation. |
Control System
| PID for automated operation, with fault alarm and parameter adjustment functions |
4.Advantages of PVC Four-Strand Conduit Extrusion
PVC four-strand conduit extrusion refers to an advanced production technology that simultaneously extrudes four PVC electrical conduits from a single extrusion line, integrating a specialized multi-cavity die, synchronized traction, and coordinated cutting systems. This innovative setup offers significant advantages over traditional single-out or double-out extrusion lines, making it increasingly favored in high-volume manufacturing. Below are its core benefits:
4.1. Dramatically Enhanced Production Efficiency
The most prominent advantage lies in its exponential output increase. By extruding four conduits in parallel, the production capacity is approximately 4 times higher than single-out lines and 2 times higher than double-out lines under the same operating conditions (e.g., extrusion speed of 10–15 m/min). For example, a standard single-out line producing 10,000 meters/day can be upgraded to 40,000 meters/day with a four-strand system, directly addressing large-order demands and shortening delivery cycles.
4.2. Reduced Unit Production Costs
While the initial investment in a four-strand line is higher, it delivers substantial long-term cost savings:
Lower Energy Consumption per Unit: A single extruder drives four dies, reducing total energy use by 30% compared to operating four separate single-out lines. For instance, heating, motor, and auxiliary equipment (e.g., cooling systems) share energy input, minimizing redundant power waste.
Optimized Labor Costs: One operator can monitor the entire four-strand line, eliminating the need for 3–4 operators required for multiple single-out lines. Labor expenses per ton of product are thus reduced by 40%.
Fixed Cost Amortization: Shared infrastructure (e.g., raw material mixing, conveying systems, and space) spreads fixed costs across more output, lowering the unit cost of each conduit.
4.3. Superior Product Consistency
Four-strand extrusion ensures uniformity across all four conduits due to:
Stable Process Parameters: A single extruder maintains consistent melt temperature, pressure, and flow rate, avoiding variations caused by separate machines in multi-line setups.
Precision Multi-Cavity Dies: Advanced die designs (e.g., balanced flow channels, uniform heating zones) ensure identical wall thickness, outer diameter tolerance (±0.3mm), and surface finish for all four conduits.
Synchronized Traction & Cutting: Coordinated traction units and rotary cutters guarantee consistent length (±2mm) and straightness, reducing post-production sorting and rework.
4.4. Space-Saving & Streamlined Workflow
A four-out line occupies 60% of the floor space required for four single-strand lines, making it ideal for factories with limited space. The compact layout also simplifies material handling (e.g., centralized raw material feeding and finished product collection), reducing logistics complexity and on-site congestion.
4.5. Stronger Market Competitiveness
High output and cost efficiency enable manufacturers to:
Meet bulk orders faster: Critical for winning contracts with construction companies or electrical distributors requiring large volumes (e.g., 100,000+ meters/month).
Offer competitive pricing: Lower unit costs allow flexibility in pricing strategies without compromising profit margins.
Adapt to demand fluctuations: Rapidly scale production up or down by adjusting extrusion speed, avoiding overcapacity risks of multiple single-out lines.
4.6. Environmental & Operational Benefits
Reduced Waste: Stable processing minimizes defective products (scrap rate<1%, vs. 3–5% for multi-line setups), lowering raw material waste.
Simplified Maintenance: Fewer total machines mean reduced upkeep tasks (e.g., fewer motors, heaters, or control systems to service), cutting maintenance time by ~50%.
Conclusion: PVC four-strand conduit extrusion represents a "high-efficiency, low-consumption" solution for modern pipe manufacturing. By maximizing output, minimizing costs, ensuring quality consistency, and saving space, it empowers manufacturers to stay competitive in fast-paced construction and electrical markets.